An evaluation tool kit of air quality micro-sensing units
B. Fishbain, U. Lerner, N. Castell, T. Cole-Hunter, O. Popoola, D.M.Broday, T. Martinez Iniguez, M. Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Jovasevic-Stojanovic, D. Topalovic, R.L. Jones, K.S.Galea, Y. Etzion, F. Kizel, Y.N.Golumbic, A. Baram-Tsabari, T. Yacobi, D. Drahler, J.A.Robinson, D. Kocman, M. Horvat, V. Svecova, A. Arpaci, A. Bartonova
Abstract
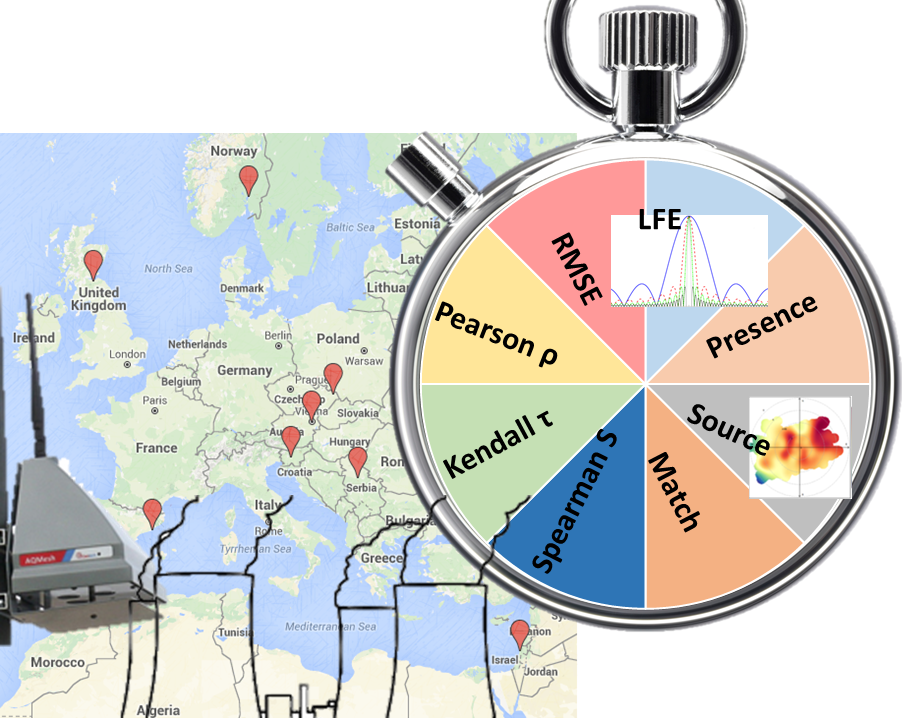 Recent developments in sensory and communication technologies have made the development of portable air-quality (AQ) micro-sensing units (MSUs) feasible. These MSUs allow AQ measurements in many new applications, such as ambulatory exposure analyses and citizen science. Typically, the performance of these devices is assessed using the mean error or correlation coefficients with respect to a laboratory equipment. However, these criteria do not represent how such sensors perform outside of laboratory conditions in large-scale field applications, and do not cover all aspects of possible differences in performance between the sensor-based and standardized equipment, or changes in performance over time. This paper presents a comprehensive Sensor Evaluation Toolbox (SET) for evaluating AQ MSUs by a range of criteria, to better assess their performance in varied applications and environments. Within the SET are included four new schemes for evaluating sensors’ capability to: locate pollution sources; represent the pollution level on a coarse scale; capture the high temporal variability of the observed pollutant and their reliability. Each of the evaluation criteria allows for assessing sensors’ performance in a different way, together constituting a holistic evaluation of the suitability and usability of the sensors in a wide range of applications. Application of the SET on measurements acquired by 25 MSUs deployed in eight cities across Europe showed that the suggested schemes facilitates a comprehensive cross platform analysis that can be used to determine and compare the sensors’ performance. The SET was implemented in R and the code is available on the first author’s website.
Recent developments in sensory and communication technologies have made the development of portable air-quality (AQ) micro-sensing units (MSUs) feasible. These MSUs allow AQ measurements in many new applications, such as ambulatory exposure analyses and citizen science. Typically, the performance of these devices is assessed using the mean error or correlation coefficients with respect to a laboratory equipment. However, these criteria do not represent how such sensors perform outside of laboratory conditions in large-scale field applications, and do not cover all aspects of possible differences in performance between the sensor-based and standardized equipment, or changes in performance over time. This paper presents a comprehensive Sensor Evaluation Toolbox (SET) for evaluating AQ MSUs by a range of criteria, to better assess their performance in varied applications and environments. Within the SET are included four new schemes for evaluating sensors’ capability to: locate pollution sources; represent the pollution level on a coarse scale; capture the high temporal variability of the observed pollutant and their reliability. Each of the evaluation criteria allows for assessing sensors’ performance in a different way, together constituting a holistic evaluation of the suitability and usability of the sensors in a wide range of applications. Application of the SET on measurements acquired by 25 MSUs deployed in eight cities across Europe showed that the suggested schemes facilitates a comprehensive cross platform analysis that can be used to determine and compare the sensors’ performance. The SET was implemented in R and the code is available on the first author’s website.
Code
Please find the R package under this link. The main file is the sensorCompareWithQi.R for data with wind info (thus, for each measurement the speed and direction).
If your data does not have wind info the main file is sensorCompareWithQiNoWind.R.
The zip file contains both sample data with and without wind info. The main files contain detailed info how to run the files.
Please cite the following paper in any future publication using this package: B. Fishbain, U. Lerner, T. Cole-Hunter, N. Castell, O. Popoola, D.M. Broday, T. Martinez Iñiguez, M. Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Jovasevic- Stojanovic, D. Topalovic, R.L. Jones, K. Galea, Y. Etzion, F. Kizel, Y.N. Golumbic, A .Baram-Tsabari, J.A. Robinson, D. Kocman, M. Horvat, V. Svecova, A. Arpaci and A. Bartonova, “An Evaluation Tool Kit of Air Quality Micro-Sensing Units”, Science of the Total Environment, 575(1):639-648, 2017.
